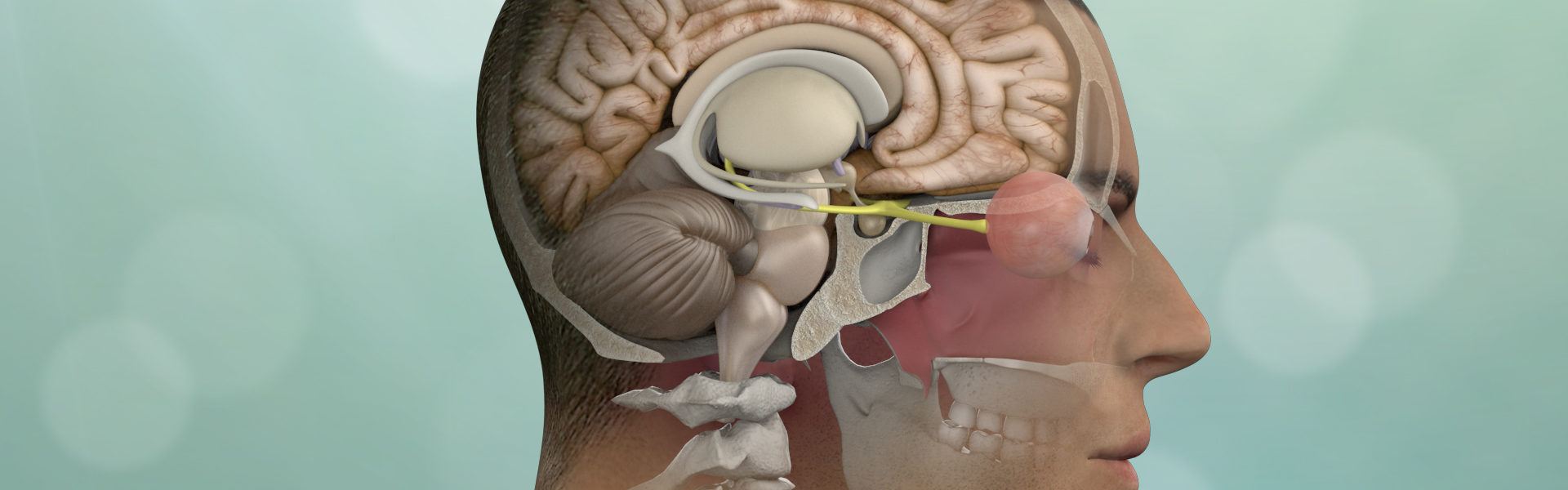
Brain Surgery
Brain surgery, also known as neurosurgery, is a medical procedure performed on the brain or surrounding tissues. It can be necessary for various conditions, including tumors, blood clots, aneurysms, epilepsy, and traumatic brain injuries. Here are some key points about brain surgery:
Types of Brain Surgery
A surgical procedure where a section of the skull is removed to access the brain. After surgery, the bone flap is usually replaced.
A minimally invasive procedure where surgery is performed through the nasal passages to access parts of the brain and skull base.
The patient is awake during surgery to help the surgeon avoid critical areas of the brain that control speech, movement, and other essential functions.
Uses a three-dimensional coordinate system to locate small targets inside the brain. It is often used for biopsy or treatment of small brain lesions.
Indications for Brain Surgery
Both malignant (cancerous) and benign (non-cancerous) tumors may require surgical removal.
Surgical clipping or endovascular coiling to prevent rupture.
To remove blood clots, relieve pressure, or repair fractures.
Shunt placement to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid.
Surgery to remove or alter the area of the brain causing seizures.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection.
Blood loss during or after surgery.
Potential for temporary or permanent changes in brain function, including memory, speech, and motor skills.
Some patients may experience seizures post-surgery.
Brain swelling, which can lead to increased intracranial pressure.